Content
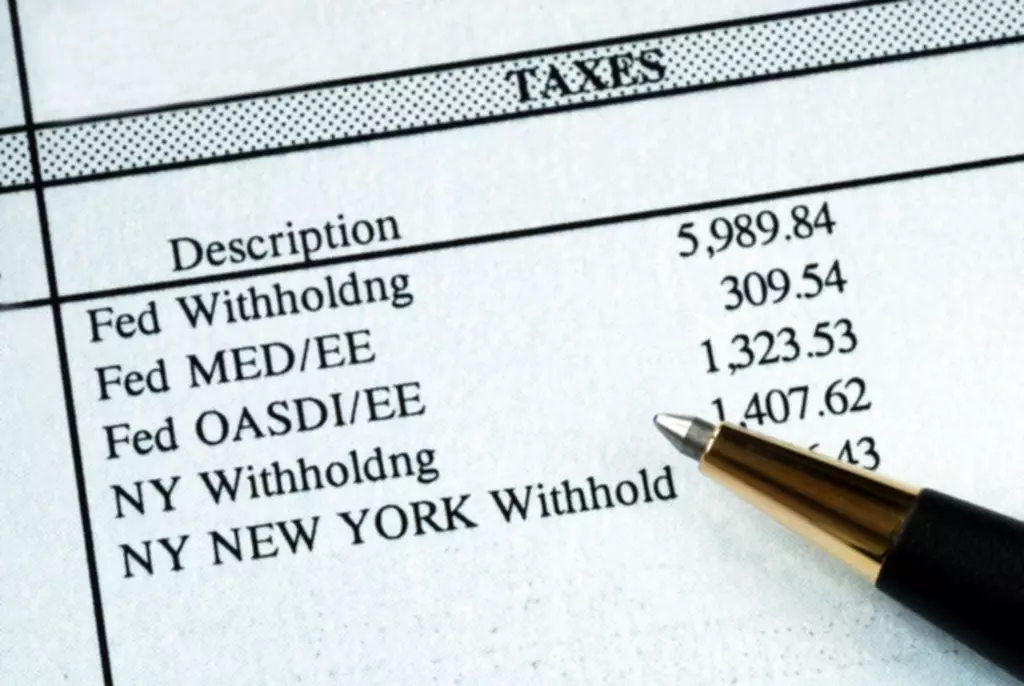
Concerning a loan, amortization focuses on spreading out loan payments over time. For tax purposes, amortization can result in significant differences between a company’s book income and its taxable income. Almost all intangible assets are amortized over their useful life using the straight-line method. This means the same amount of amortization expense is recognized each year.
Accordingly, the carrying amount may differ from the market value of assets. Amortization https://www.bookstime.com/ is a mechanism that can apply to both companies and personal finance.
How to Calculate Capitalized Interest on Assets
Examples of the kind of assets that impact this kind of amortization are goodwill, a patent or copyright. Record amortization expenses on the income statement under a line item called “depreciation and amortization.” Debit the amortization expense to increase the asset account and reduce revenue. A loan doesn’t deteriorate in value or become worn down over use like physical assets do. Loans are also amortized because the original asset value holds little value in consideration for a financial statement. Though the notes may contain the payment history, a company only needs to record its currently level of debt as opposed to the historical value less a contra asset.
Depreciation is an accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life to account for declines in value over time. The two basic forms of depletion allowance are percentage depletion and cost depletion.
Step 2: Calculate the period interest rate.
CAPEX loans for PP&E and commercial mortgages) is repaid by periodic payments, sometimes called installments. In general, amortization schedules are provided to borrowers by banks or other financial institutions when credit is extended so that borrowers understand the repayment structure. Under GAAP, for book purposes, any amortization startup costs are expensed as part of the P&L; they are not capitalized into an intangible asset. Calculating amortization requires estimating the useful life of an asset. When a company acquires a rival and its patents, the company can immediately amortize what it estimates to be the lifespan of the patents over a period.
Another difference is the accounting treatment in which different assets are reduced on the balance sheet. Amortizing an intangible asset is performed by directly crediting that specific asset account. Alternatively, depreciation is recorded by crediting an account called accumulated depreciation, a contra asset account. The historical cost fixed assets remains on a company’s books; however, the company also reports this contra asset amount to report a net reduced book value amount. These loans, which you can get from a bank, credit union, or online lender, are generally amortized loans as well. They often have three-year terms, fixed interest rates, and fixed monthly payments. For example, a $100,000 mortgage will have a higher monthly payment at a15-year term than a 30-year term, but you’ll pay much more in interest for a 30-year term than a 15-year term.
Amortization Meaning: Definition and Examples
The useful life, for book amortization purposes, is the asset’s economic life or its contractual/legal life , whichever is shorter. For book purposes, companies generally calculate amortization using the straight-line method. This method spreads the cost of the intangible asset evenly over all the accounting periods that will benefit from it. Amortization is the accounting process used to spread the cost of intangible assets over the periods expected to benefit from their use. Loan amortization, a separate concept used in both the business and consumer worlds, refers to how loan repayments are divided between interest charges and reducing outstanding principal. Amortization schedules determine how each payment is split based on factors such as the loan balance, interest rate and payment schedules. Amortization, like depreciation, is a non-cash expense because the value of the asset is written down over a period, but it does reduce earnings on the income statement.
