But the filings take time to publish, and as such, an investor comes to know about the book value of a company after a significant amount of time from the actual event. Decides to sell the same laptop in an open market after 1 year it might only fetch 20,000. The maximum amount a buyer is willing to pay for the laptop after one year is its how to calculate book value market value. For example, a business that owns a laptop for 50,000 lasts for five years. After the end of the 1st year, its net book value will be 50,000 – 20%, i.e. 40,000. Net Book Value helps in reflecting the value of an unutilized asset as on a given date because of which, it is also termed as Net Asset Value or Carrying Value.
It helps in estimating the real value of the assets which also helps in business valuation at the time of liquidation of the company. Example 1 – Suppose a company purchases a pre-owned truck worth 80,000 & further, incurs a cost of 10,000 for its repairs before using it. Also, it decides to charge depreciation @ 10% as per the straight-line method. The book value shown on the balance sheet is the book value for all assets in that specific category. Book value does not need to be calculated for more stable assets that aren’t subject to depreciation, such as cash and land. Depreciable assetshave lasting value, and they include items such as furniture, equipment, buildings, and otherpersonal property.
StockholdersA stockholder is a person, company, or institution who owns one or more shares of a company. They are the company’s owners, but their liability is limited to the value of their shares. Also, we can add Equity Share capital and Reserves to get shareholder’s equity which is 5,922 cr + 2,87,569 cr, which will sum to 2,93,491 cr. Written-down value is the value of an asset after accounting for depreciation or amortization.

After 2 years, the company revalued the asset and its revised value at the end of the 2nd year turns out to be 1,40,000. Its remaining useful life was re-estimated at 5 years with nil salvage value. Step 3 – Subtract accumulated depreciation from the historical cost of the asset. Net Book Value represents the carrying value of an asset that is equal to the value after deducting depreciation, depletion, amortization and/or accumulated impairment, to date. It is the value at which an asset is recorded in the balance sheet of an enterprise. A P/B ratio below 1 often indicates that a company’s stocks are undervalued since its market capitalisation is lower than its book value.
It is the profit a company gets when it issues the stock for the first time in the open market. The price-to-book value ratio, also known as the price-equity ratio, is also derived from the book value of an organisation. P/B ratio shows the relationship between a company’s market capitalisation and its book value. In personal finance, the book value of an investment is the price paid for a security or debt investment. When a company sells stock, the selling price minus the book value is the capital gain or lossfrom the investment. Also known as the price-equity ratio, is also derived from the book value of an organization.
When you sell your investments in a non-registered account, book value is used to determine your capital gain or capital loss for tax purposes. The book value of a company is the difference between that company’s total assets and its total liabilities, as shown on the company’s balance sheet. We offer a 21st-century e-commerce experience for automobiles and is one of the leading e-commerce platforms for used cars sales in India. We have expanded our platform to include over 11 vehicle categories, sold by auto dealers and individual sellers in 1,151 cities in India.
According to conventional accounting approaches, most assets’ values are represented as per their historical figures. It does not account for the actual depreciation and appreciation in values of assets but instead is based on set accounting principles. This phenomenon creates a discrepancy and compromises analysis based on book value.
What’s a Good P/B Ratio?
Price-to-book (P/B) ratio as a valuation multiple is useful for value comparison between similar companies within the same industry when they follow a uniform accounting method for asset valuation. It provides services in the area of investment banking, commercial banking, and treasury services, among others. However, during the stock market crash of March 2020, the stock price declined by around 40%. You will need the number of shares outstanding obtained from the income statement. Also, you can use our handy market cap calculator to obtain the value.
Book Value Per Share The book value per share formula evaluates the actual value of the common equity for each outstanding share, excluding the preferred stock value. A higher BVPS compared to the market value per share indicates an overvaluation of stocks and vice-versa. For example, real estate owned by a company may gain in market value at times, while its old machinery can lose value in the market because of technological advancements. In these instances, book value at the historical cost would distort an asset or a company’s true value, given its fair market price. However, Total equity is not the book value that matters for stockholders. Consequently, it is better to go directly to the equity side of the balance sheet.
For instance, in the semiconductors industry, several companies have so much value in intangible assets that the tangible book value of equity turns negative. It is worth mentioning that the asset value recorded in the balance sheet is discounted by its depreciation period by period; thus, we should expect a decreasing equity value over time. That can happen; however, in successful companies, when the return on assets is high, constant, and stable, the depreciation effect is offset by the cash retained from the company. The first equation deducts accumulated depreciation from the total assets to get the book value amount. Accumulated Depreciation is the cumulative wear and tear that an asset goes through during a certain period of time. Accumulated depreciation is calculated by adding depreciation from all the previous years.
Based on that, they can gauge whether stock prices will go down or up in the future. DividendDividends refer to the portion of business earnings paid to the shareholders as gratitude for investing in the company’s equity. It serves as the total value of the company’s assets that shareholders would theoretically receive if a company was liquidated.
How to use the price to book ratio formula
The book value of a company is the total worth of all its assets minus all its liabilities. Investors looking for low-priced but fundamentally sound stocks use a company’s book value to see if its shares are fairly priced. Is marked to market, i.e., it captures the most current market value of the assets and liabilities.
- In accordance with the cost principle of accounting, assets are always listed in the general ledger at cost; this helps create consistency in reporting standards.
- To exemplify this method further, the depreciation expense in the second year would be based off of the first year-end book value, which is $10,000-$2,000, or $8,000.
- If book value is negative, where a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, this is known as a balance sheet insolvency.
- Some sites also list this as a single figure, called the price-to book ratio.
- In that sense, the price-to-book ratio compares the book value vs. the market value, showing us the market’s appreciation towards a company.
Market value is another important metric; however, NBV and market value typically aren’t equal. Liquidation, or if another company is considering taking over the business. In our example, the NBV of the logging company’s truck after four years would be $140,000.
The major limitation of the formula for the book value of assets is that it only applies to business accountants. The formula doesn’t help individuals who aren’t involved in running a business. The book value of assets is important for tax purposes because it quantifies the depreciation of those assets. Depreciation is an expense, which is shown in the business profit and loss statement. Depreciation effectively lowers profits, thereby reducing business taxes.
Sales tax
TheNet Book Value describes the carrying value of an asset recorded on a company’s balance sheet for bookkeeping purposes. This is an accelerated depreciation method that expenses more depreciation at the beginning of the life of an asset than at the beginning. This rate is found by multiplying the straight line percentage of depreciation. For example, double-declining depreciation for asset with a 10-year life would be 2 x 10%, or 20%. This means that the new book value at the end of an accounting period would be 20% less than the previous book value.
Is the amount that an asset will bring if it is sold in the market today. It is the price that people are willing to pay in an open market for an asset. Step 1 – Find the historical cost of the asset by computing its total cost of acquisition. The book value of an asset isn’t helpful for individuals—while the formula still works, the tax benefits don’t extend beyond business assets. The book value of an asset is an accounting calculation that measures the impact of depreciation on an asset’s value.
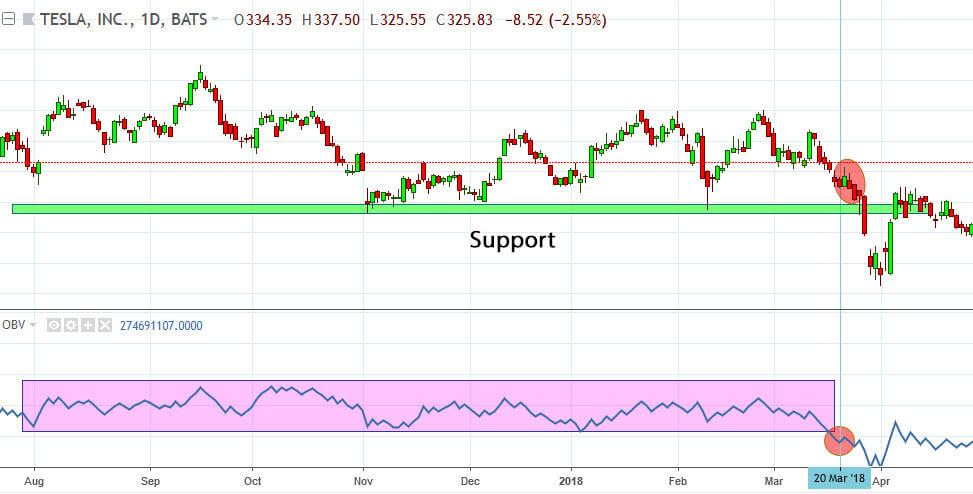
Enjoy the perks of seamless tech integration with OBV
Intangible assets and liabilities are deducted from the total asset amount to calculate the book value of the asset. One example of an intangible assets is intellectual property, like music, digital artwork, etc. Liabilities are the outstanding obligations that a company has to pay back within a limited period of time. When calculating the book value per share of a company, we base the calculation on the common stockholders’ equity, and the preferred stock should be excluded from the value of equity.
What is the P/E ratio? An analytical tool that helps you decide if a stock is a good buy at its current price
This sum aims to put a number on what a company’s actually “worth.” It’s the amount that theoretically represents the company’s breakup value. If the company went under or was dismantled and sold off, this book value would be used to determine what individual stockholders would receive – roughly, the cash value of their individual shares. Book value works best on hard-goods companies, vs service providers or firms with intangible assets. Market capitalisation is the product between the total number of outstanding shares of an organisation and its current market price.
